展示使用版本为2015-2 (集群上). 先了解图形界面化下的可用项, 再了解命令行选项.
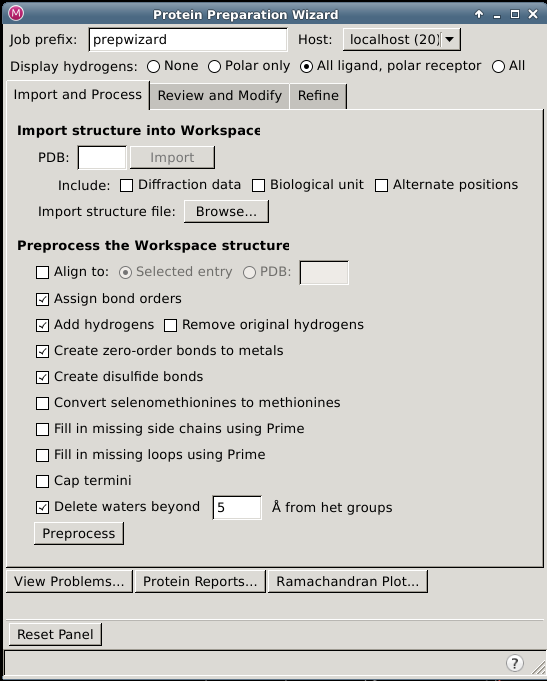
Protein Preparation Wizard – Import and Process Tab
Summary
In this tab you can import a structure if there is not already a structure in the Workspace, select options to amend the structure, and perform the basic preparation tasks.
Note: You should always check that the structure is correct after any automatic procedure is run.
进行基础的蛋白结构预处理工作.
Import and Process Tab Features
Import structure into Workspace section
The Protein Preparation Wizard uses the structure in the Workspace as its input. The import controls are provided so you can conveniently load a structure from an external source. These allow you to obtain a protein structure from a file or from the PDB. The structure is imported into the project as a project entry, and replaces the Workspace.
PDB text box
Enter the PDB ID of the protein you want to retrieve in this text box.
Include options
These options allow you to choose extra data from the PDB to download along with the structure:
- Diffraction data option Select this option to download the X-ray diffraction data as well as the structure. This is particularly useful for PrimeX.
- Biological unit option Select this option to download the biological unit from the PDB rather than the regular PDB file. All structures in the biological unit are merged into a singe project entry on import. This option requires an internet connection.
- Alternate positionsSelect this option to include alternate positions of the atoms in the structure. By default only the highest occupancy position is downloaded.
Import button
Click this button to import the specified protein from your local copy of the PDB, with a fallback to downloading from the PDB web site. If you want to download the protein from the PDB web site, you can use the Get PDB File dialog box to download the file, then import it by clicking Browse in the Protein Preparation Wizard panel.
Browse button
Clicking this button opens the Import panel, in which you can navigate to the desired file and import it.
Preprocess the Workspace structure section
In this section you select options to amend the structure and perform the basic preparation tasks. A new entry is created for the preprocessed structure, which is colored by element.
Align to options
Align the protein structure to a reference structure using the structalign program, with the default settings. This option has two associated options for selection of the reference structure:
- Selected entryUse the entry that is selected in the Project Table for the reference structure. There must be only one entry selected in the Project Table.
- PDBUse the protein from the PDB whose 4-letter ID is given in the text box.
See the Protein Structure Alignment Panel topic for more information.
对齐蛋白到指定蛋白. 默认关闭. 对应命令行相关: -reference_st_file REFERENCE_ST_FILE, -reference_pdbid REFERENCE_PDBID
Assign bond orders option
Assign bond orders to all bonds in the structure, including het groups. This option performs the same task as Assign Bond Orders on the Tools menu.
键级指认. 默认开启, 关闭对应: -nobondorders选项
Add hydrogens option
Add hydrogens to all atoms in the structure that lack them. The hydrogens are added by the utility applyhtreat.
缺氢的加氢, 默认开启. 关闭对应: -nohtreat 选项
Remove original hydrogens option
Remove the original hydrogens before adding hydrogens to the structure. This option allows any problems with hydrogen atoms in the original structure to be fixed, including nonstandard names, which prevent proper H-bond assignment.
重新加氢, 默认关闭. 开启对应: -rehtreat 选项
Create zero-order bonds to metals option
Break bonds to metals and corrects the formal charge on the metal and the neighboring atoms, then add zero-order bonds between the metal and its ligands, so that it is still considered part of the same molecule.
创建金属0级键, 默认开启. 关闭对应: -nometaltreat 选项
Create disulfide bonds option
Find sulfur atoms that are within 3.2 of each other, and add bonds between them. CYS residues are renamed to CYX when the bond is added. This option is selected by default.
二硫键识别和处理, 默认开启. 开启对应: -disulfides 选项
Convert selenomethionines to methionines option
This option converts selenomethionines (MSE) to methionines (MET), and is not selected by default. A dialog box opens to inform you if any conversions are done.
转换MSE到MET, 默认关闭. 开启对应: -mse 选项
Fill in missing side chains using Prime option
Run a Prime refinement job (refinestruct) to place and optimize the missing side chains. See the Predict Side Chains Panel topic for more information.
补全缺失的侧链(Prime), 默认关闭. 开启对应: -fillsidechains 选项
Fill in missing loops using Prime option
Fill in missing loops from the SEQRES records in the PDB file. Requires Prime. The resulting loop may not be of high quality, and a Prime loop refinement should be performed to obtain higher quality. See the Refine Loops Panel topic for details.
补全缺失的Loop区(Prime),会从PDB文件SEQRES部分查找序列信息. 默认关闭. 开启对应: -fillloops 选项. 在命令行可以用-fasta_file CUSTOM_FASTA_FILE指定序列的fasta文件.
Cap termini option
Add ACE (N-acetyl) and NMA (N-methyl amide) groups to uncapped N and C termini. These termini include any chain breaks.
N-C末端增加新残基封端, 默认关闭. 开启对应: --c, -captermini 选项
Delete waters beyond N from het groups option and text box
Delete waters that are more than the specified distance (in angstroms) from any het group.
You can also delete waters individually in the Review and Modify tab, and you can delete waters that do not form H-bonds with non-waters in the Refine tab.
删除配体分子一定距离N 埃以外的水分子, 默认开启. 关闭对应: --keepfarwat 选项, 删除配体距离截断为-watdist WATDIST (默认5 A)
Preprocess button
Prepare the structures using the options selected in this section. The progress of the structure correction is displayed at the foot of the panel. When all operations are finished, a new entry is created and a color scheme is applied to the structure. The tables in the Review Structure tab are filled in, and if any problems are found with the structure, the Protein Preparation - Problems dialog box is displayed, listing the problematic atoms or residues.
处理结构, 只进行该Tab部分的处理.
View Problems button
Open the Protein Preparation - Problems dialog box, which contains tables of residues that have missing atoms, overlapping atoms, and atoms that are incorrectly typed. The Workspace structure is analyzed to detect these problems before opening the dialog box. You can click on a row in any of the tables in the dialog box to zoom in on the atoms or residues listed in that row. To fix a problem, you can use any of the Maestro capabilities.
查看当前蛋白存在的问题, 如缺失原子, 原子冲撞, 类型错误等.
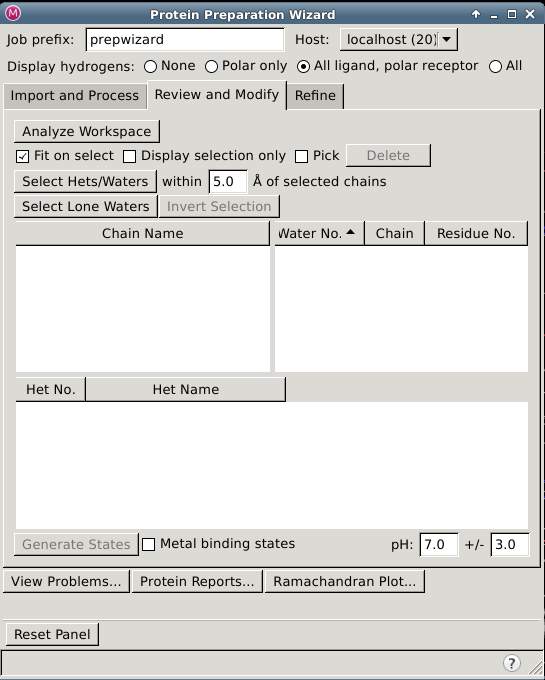
Protein Preparation Wizard —- Review and Modify Tab
Summary
In this tab you can inspect parts of the structure in the Workspace by selecting them in tables, deleted unwanted parts, and generate ionization, tautomeric, and metal-binding states for het groups.
When you select a chain, water, or het group, the color scheme with green carbons is used for the selected atoms, and the color scheme of the unselected atoms is changed to darker colors so that the selected atoms stand out. The selection also computes and displays hydrogen bonds between the selected and the unselected atoms.
进行基于人为查看和选定来进行修补工作.
Review and Modify Tab Features
Analyze Workspace button
Analyze the Workspace structure to identify chains, waters, and het groups, and fill the tables with the results. If you clicked Preprocess in the Import and Process tab, the analysis is done automatically. This button is intended for working with structures that have already been preprocessed to fix any issues with the structure.
Fit on select option
Fit the selection to the size of the Workspace when you select chains, waters, or hets.
Display selection only option
Display only the selected chains, waters, and hets.
Pick option
Select this option to pick chains, waters, or hets in the Workspace. The picked objects are selected in the tables. You can use shift-click to add to the selection and control-click to change the selection of an object without affecting the selection of other objects.
Delete button
Delete the selected chains, waters, and hets.
Select Hets/Waters within N Å of selected chains button and text box
Select het groups and waters within the specified distance of the chains that are selected. This feature is useful for reducing a multimer to a monomer: select the chain, select the het groups/waters, invert the selection and then delete.
Select Lone Waters button
Select waters that have nothing other than waters within 5 Å.
Invert Selection button
Invert the selection of chains, waters, and hets. This is useful for selecting the parts that you want, then deleting the rest (by inverting the selection, then clicking Delete).
Chains table
This table lists the chains in the Workspace. The chains are listed by the chain letter, with a blank name shown in quotes. You can select multiple chains in the table for application of an action.
Waters table
This table lists the waters in the Workspace. A serial number and the residue number are given in the table. You can select multiple waters in the table for application of an action.
Hets table
This table lists the het groups in the Workspace. A serial number and the het name are given in the table by default. The het name consists of the chain name, residue name, and residue number for each residue in the het group. You can select multiple hets in the table for application of an action.
When ionization and tautomeric states have been generated, Sn (state) columns are added to the het groups table and are populated with check boxes for the selection of the state. The column for the original state is marked Orig. The selected state is displayed in the Workspace, with markers to indicate the atoms that differ between states. When you select a state, the status area at the foot of the panel displays the state penalty, the tautomer probability, the charge, and the number of hydrogen bonds made to the het group. The state that is selected by default is the state with the lowest penalty (and if there is more than one such state, it is the state with the most H-bonds).
Generate States button
Run Epik to generate probable ionization and tautomeric states in the pH range specified for all het groups. The calculation may take a few minutes. When it finishes, the table rows for the het groups are populated with check boxes, which you can use to select the desired state. The het states are labeled with formal charges on charged atoms.
用Epik对配体的质子化状态和共振态进行计算. 在图形界面为人为选择. 命令行默认开启, 关闭对应: -noepik
Metal binding states option
When Epik is run, include generation of states for binding to metals in metalloproteins.
产生结合到金属蛋白的状态. 默认关闭. 命令行开启对应: -metal_binding
pH text boxes
Enter the target pH and pH range for the generation of probable ionization and tautomeric states in these text boxes.
可能质子化状态的pH范围. 命令行没有对应选项.
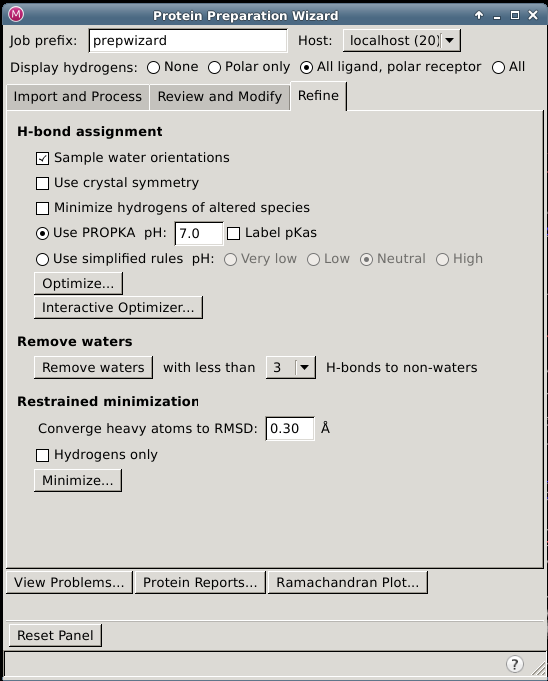
Protein Preparation Wizard — Refine Tab
Summary
In this tab you can refine the assignment of hydrogen bonds, including terminal chi flips and histidines, remove waters based on their hydrogen bonding pattern, and perform a restrained minimization.
进行进一步的修正, 包括H键网络优化, 去除水分子, 受限制优化等.
Refine Tab Features
H-bond assignment section
In this section, you can optimize the hydrogen bonding network and the orientation of Asn, Gln, and His residues, either interactively or automatically as a job. Both choices use the same underlying technology. A new entry is created for the optimized structure.
These optimizations are necessary because the orientation of hydroxyl (or thiol) groups, the terminal amide groups in asparagine (Asn) and glutamine (Gln), and the ring of histidine (His), cannot be determined from the X-ray structure. Flipping the terminal amide groups and the histidine ring can improve charge-charge interactions with neighboring groups as well as improving hydrogen bonding. The 180° flips preserve the heavy-atom placement deduced from the X-ray electron density. In addition, the protonation state of histidine is varied to optimize hydrogen bonding and charge interactions.
If waters are included with the protein structure, their orientations are also varied to optimize hydrogen bonding.
Sample water orientations option
Select this option to sample water orientations when running the H-bond optimization. Deselect this option if the water molecules are already optimally placed, and you only want to run the other optimizations.
水分子优化H键网络. 默认开启, 命令行开启对应: -s, -samplewater
Use crystal symmetry option
Use crystal symmetry when optimizing the H-bond network.
使用晶体对称性进行H键网络优化. 默认关闭. 开启命令行对应: -xtal
Minimize hydrogens of altered species option
Perform a minimization for hydrogens that were adjusted during the sampling.
是否对重新采样的氢原子进行优化. 默认关闭. 没有对应命令行选项因为都会进行后续优化????
Use PROPKA; pH options
Perform the H-bond optimization with protonation states of residues at a given pH, as determined from a pKa prediction by PROPKA. The associated Label pKas option allows you to label the atoms in the protein with their predicted pKa values.
使用PROPKA预测残基pKa,再根据给定pH比较判断质子化状态. 后一个选项可以标记pKa到残基. 默认开启, pH为7. 命令行对应: -propka_pH PROPKA_PH, 标记pKa对应: -label_pkas
Use simplified rules options
Perform the H-bond optimization with protonation states of residues in a given pH range. The options perform the following actions, relative to the normal biological pH of 7. - very low—protonate ASP, GLU, HIS - low—protonate HIS - neutral—normal biological states - high—deprotonate CYS
使用预定义规则对残基进行质子化, 对应状态有四种. 该选项和 Use PROPKA 冲突!!!! 默认不适用. 命令行对应: -pH PH和-nopropka合用.
Optimize button
Run a job to optimize the hydrogen bonding network. The tasks include optimizing the orientation of hydroxyl groups, performing 180° flips of the amide groups of asparagine and glutamine and the ring of histidine, and adjusting the charge state of histidine residues. The job then orients water molecules to optimize hydrogen bonding. This is an iterative process, which passes over all the groups whose H-bonds need to be optimized multiple times.
Note: If you have a lot of water molecules in the structure, this process can take a long time. You should ensure that you have deleted unwanted waters before you start this process.
进行氢键网络优化操作. 人为控制. 命令行默认开启, 关闭对应: -noprotassign
Interactive Optimizer button
Opens the Interactive H-bond Network Optimizer panel, in which you can examine each assignment of terminal group or hydroxyl orientation and select the desired orientation.
Remove waters section
Once the hydrogen-bonding network has been refined, you can choose to retain or remove waters based on the number of hydrogen bonds they form with parts of the structure that are not other waters. This allows you to keep waters that have significant binding to the receptor, for example, forming bridges, and remove the rest of the waters. To do so, choose the minimum number of hydrogen bonds from the Remove waters with less than N H-bonds to non-waters option menu, and then click Remove Waters. This is an alternative to keeping waters based on the proximity to the ligand, or manually removing waters.
去除少于具有指定氢键数的水分子, 在ProtAssian后可选进行. 命令行对应: -delwater_hbond_cutoff DELWATER_HBOND_CUTOFF. 命令行指定后会进行该操作, 图形界面默认3.
Restrained minimization section
This section provides controls for optimizing the corrected structure, to relieve any strain and fine-tune the placement of various groups. Hydrogen atoms are always optimized fully, which allows relaxation of the H-bond network. Heavy atoms can be restrained, so that a small amount of relaxation is allowed, or they can be kept fixed. These parts of the process are run as jobs under Job Control, since they are more time-consuming than the earlier parts of the procedure. A new entry is created for the minimized structure.
Converge heavy atoms to RMSD text box
Specify the RMSD of the heavy-atom displacement below which the minimization is terminated.
重原子位移RMSD收敛标准, 默认0.3. 命令行开启对应: -fix 选项.
Hydrogens only option
Select this option if you want to leave heavy atoms in place in the minimization, and only optimize the hydrogen atom positions. Allowing some movement of the heavy atoms can relieve structural strain, but will result in some deviation from the input structure.
只进行氢原子的优化(限制重原子不动). 默认关闭. 命令行开启对应: -r RMSD, -rmsd RMSD 选项.
Force field option menu
Select the force field to be used in the minimization. The default can be set under Jobs – Force field in the Preferences panel.
选择优化的力场(但实际无显示), 可以在命令行用-f FORCE_FIELD控制, 可选OPLS力场为2005(缺省)和2.1
Minimize button
Perform a restrained minimization of the protein structure, using impref.
进行限制结构优化(impref). 手动控制. 命令行默认开启, 关闭对应-noimpref选项.
Related Topics:
- Protein Preparation Wizard Panel
- Epik Panel
- Protein Reports Panel
- Ramachandran Plot Panel
- Interactive H-bond Network Optimizer Panel
prepwizard command
Schrodinger 2015-2: prepwizard -h
Usage: $SCHRODINGER/utilities/prepwizard [options] inputfile outputfile
Input file should be in Maestro or PDB format.
Output file should be in Maestro or PDB format.
Options:
-v, -version Show the program's version and exit.
-h, -help Show this help message and exit.
-nobondorders Don't assign bond orders to het groups
-nohtreat Don't add hydrogens
-rehtreat Delete and re-add hydrogens (will reset PDB atom
names)
-c, -captermini Cap termini
-keepfarwat Don't delete waters far from het groups
-watdist WATDIST Distance threshold for 'far' waters (default 5A)
-nometaltreat Don't treat metals (adding zero-order bonds, etc)
-disulfides Create bonds to proximal Sulfurs (delete hydrogens as
needed)
-mse Convert Selenomethionine residues to Methionines
-fillsidechains Fill missing side chains Prime
-fillloops Fill missing loops with Prime
-fasta_file CUSTOM_FASTA_FILE
If filling missing residues, the custom fasta file to
use. If not specified, the fasta file will be
generated from the sequence that was stored in the
input structure when it was converted from the PDB
format.
-noepik Don't run Epik on het groups
-ms MAX_STATES Maximum number of states to generate for each het
group when running Epik.
(该选项指定最大产生的可能状态数, 图形界面没有)
-metal_binding User Epik's metal binding mode
-noprotassign Don't run ProtAssign
-s, -samplewater ProtAssign: sample waters
-xtal ProtAssign: Use crystal symmetry
-pH PH ProtAssign: Sample at given pH ('very_low', 'low',
'neutral', 'high')
(注意, 图形界面该选项和propka_pH选项是冲突的,对应用-nopropka)
-propka_pH PROPKA_PH ProtAssign: Run PROPKA at given pH value
-nopropka ProtAssign: Do not use PROPKA for protonation states
-label_pkas ProtAssign: Label residues with PROPKA pKas
-force FORCE_LIST ProtAssign: Force a particular residue to adapt the
specified state. Multiple -f specifications are
permitted. See $SCHRODINGER/utilities/protassign help
for more info.
(该选项指定残基状态, 上面没有介绍.)
-delwater_hbond_cutoff DELWATER_HBOND_CUTOFF
If specified, delete waters that do not make at least
this number H-bonds to non-waters. By default, this
feature is disabled. This step is ran after
ProtAssign.
-noimpref Don't run a restrained minimization job
-r RMSD, -rmsd RMSD Minimization: RMSD cuttoff (default 0.3)
-fix Minimization: Fix heavy atoms (minimize hydrogens
only)
-f FORCE_FIELD Minimization: Version of the OPLS force field to
use. Options: 2005 or 2.1. Default is 2005.
-reference_st_file REFERENCE_ST_FILE
File containing reference structure to align to.
-reference_pdbid REFERENCE_PDBID
PDB ID of the structure to align to.
-j JOBNAME Jobname to use. By default, jobname is based on the
input file.
(该选项指定任务名, 对应图形界面的Job Prefix.)
-NJOBS NJOBS Number of jobs to create (default 1)
(该选项指定任务数(多核运行).注意文件格式是否支持多核运行.)
Job Control Options:
-HOST <hostlist> Run job remotely on indicated host entries.
<hostlist> is a comma-separated list of one or more
schrodinger host file entry names. The number of
processors the host may use for the job can be
specified after a colon. The default number of
processors is one. Example:
"name1:nprocs1,name2:nprocs2,..." Default:
"localhost:1".
-WAIT Do not return a prompt until the job completes.
-LOCAL Do not use a temporary directory for job files. Keep
files in the current directory.
-NOLOCAL Use a temporary directory for job files.
-D, -DEBUG Show details of Job Control operation.
-NICE Run the job at reduced priority.
-SAVE Return zip archive of job directory at job completion.
-NOJOBID Run the job directly, without Job Control layer.
例子:
在MM/GBSA Binding Energy Prediction on the PDBbind Data Set: Successes, Failures, and Directions for Further Improvement 这篇paper里用到schrodinger进行复合物预处理并用里面的mmgbsa模块进行计算. 里面的处理部分描述:
……In the previous publication all complexes with ligands of a molecular weight larger than 900 (mostly polypeptides), with more than 20 donors and acceptors (mostly polyglycosides), and those with more than oneP atom (mostly NADPH and ADP/ATP) were removed.
The protein complexes were prepared using Schrodinger’s Protein Preparation Wizard with all options switched on, i.e. adding hydrogens, assigning disulfide bonds, removing waters further than 5 Å from the ligand, adjusting charges, capping termini, adding missing side-chains using Prime, optimizing hydrogen bond clusters, and performing a restrained minimization using the OPLS2005 force-field on the whole protein/ligand complex. During the minimization the heavy atoms were restrained to remain within a 0.3 Å root-mean-square deviation ofthe original PDB structure. Cases where the protein preparation wizard produced an error were individually inspected and either manually corrected or dropped.
All ligands as given in SD files in the PDBbind database were additionally scanned by RDKit, and cases where RDKit reported an error were either corrected or dropped. This left an overall number of 1387 complexes, of which 1137 complexes were processed without error by the KNIME protocol. For the further analysis all (143) complexes with ions in the binding site were removed………..
第二段描述了使用 Protein Preparation Wizard 进行处理. 根据描述(其实他应该没有补全loop), 对应操作有:
adding hydrogens (default), assigning disulfide bonds(default), removing waters further than 5 Å from the ligand (default), adjusting charges (没有该功能, 或者指formal charge?), capping termini (-c), adding missing side-chains using Prime (-fillsidechains), optimizing hydrogen bond clusters(-s -propka_pH 7.0), and performing a restrained minimization (OPLS-2005, cutoff 0.3 A) (default).
对应命令行应为:
prepwizard -c -fillsidechains -s -propka_pH 7.0 input.pdb output.pdb
Notes:
multicore processing for PDB writer KB-1523
I am trying to run the Protein Preparation Wizard from the command line with -NJOBS for multicore processing but I am getting this error message:
PDB format is not supported for StructureWriter RuntimeError: PDB format is not supported for StructureWriter
What is the problem?
It looks like you had the output file format set to PDB (filename.pdb). For multi-structure processing, you will have to set the output format to Maestro (filename.mae), as multi-structure PDB files are not supported.
The -NJOBS option is used to distribute the preparation of multiple proteins. The input file must be a multi-structure Maestro file. So, as an example, if you had a Maestro file with 3 proteins (3_pdb.mae) to be prepared, you could run a command like this:
$SCHRODINGER/utilities/prepwizard -NJOBS 3 -HOST MY\_HOST:3 3\_pdb.mae 3\_pdb\_prep.mae
in order to distribute the job over three processors on MY_HOST.
alternate side-chain conformations KB-357
Are alternate side-chain conformations considered when using the Protein Preparation Wizard?
No, the Protein Preparation Wizard only considers one conformation, as do almost all of our programs. If alternate positions might be relevant for binding, we suggest preparing a second conformation of the receptor with the alternate side-chain positions. If your protein has both sets of coordinates, you select the alternate positions you want to use in the Protein Preparation - Problems dialog box. You can also can switch to the alternate positions in Maestro by selecting the atoms that have alternate positions, then right-clicking and choosing Switch Alternate Positions from the shortcut menu.